In the 21st-century learning environment, academic proficiency alone is no longer sufficient for success. The modern world demands individuals who can understand themselves, navigate relationships, adapt to change, and make thoughtful decisions. This is where Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) becomes a transformative force. When combined with the capabilities of educational technology, SEL takes on new dimensions—making emotional intelligence more accessible, measurable, and deeply embedded in everyday learning experiences.
This article explores how empathy and innovation intersect when SEL is integrated with educational technology, examining its core principles, digital applications, and the long-term benefits for learners, educators, and society.
Understanding Social and Emotional Learning
Social and Emotional Learning is a structured, ongoing process through which individuals develop the ability to manage emotions, establish positive relationships, demonstrate empathy, and make responsible choices. According to widely accepted frameworks, Social and Emotional Learning is built around five interconnected competencies:
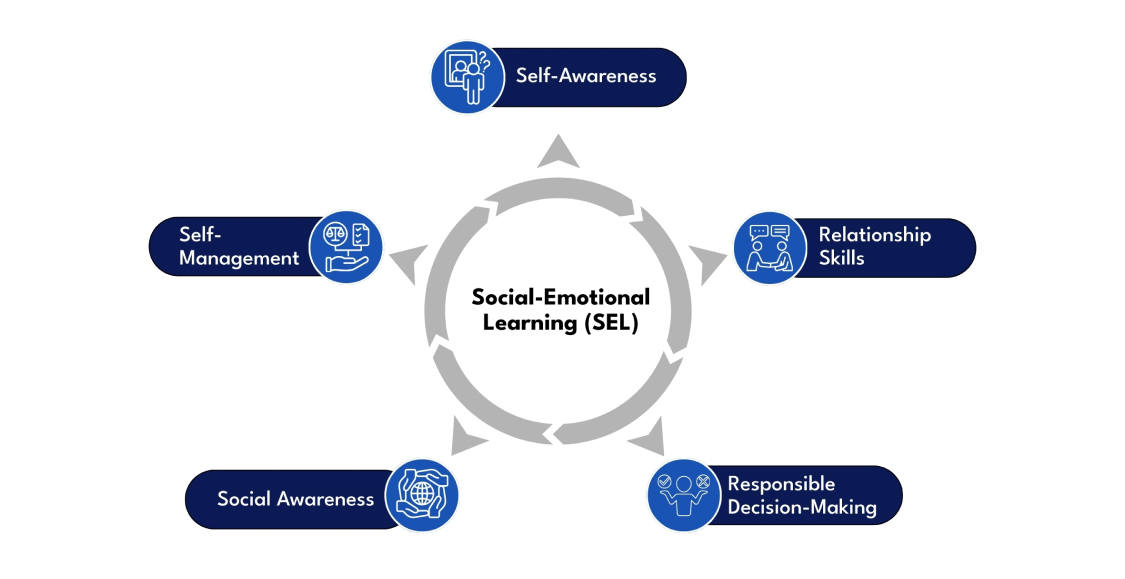
- Self-Awareness – The ability to recognize and understand one’s own emotions, values, and strengths, as well as areas for growth. This awareness helps learners identify triggers, celebrate personal achievements, and align their actions with their principles.
- Self-Management – The capacity to regulate emotions, control impulses, manage stress, and persevere in the face of challenges. This includes goal-setting and using strategies such as mindfulness to maintain focus and calm.
- Social Awareness – Understanding and appreciating the perspectives and emotions of others, recognizing social norms, and showing respect for diversity. It enables learners to adapt their behavior across different cultural or social contexts.
- Relationship Skills – The ability to form healthy, meaningful connections, communicate clearly, work cooperatively, and resolve conflicts constructively. Strong relationship skills support teamwork both inside and outside the classroom.
- Responsible Decision-Making – Making ethical, constructive choices based on the consideration of safety, societal norms, and the well-being of oneself and others. This includes critical thinking and anticipating the consequences of actions.
The integration of these competencies into everyday learning experiences builds a foundation for emotional intelligence, equipping individuals with lifelong tools for personal and professional success.
Why Social and Emotional Learning Matters in Today’s World
The pace of social, technological, and economic change means that learners must do more than acquire knowledge—they must also navigate uncertainty and complexity with resilience. SEL directly addresses this challenge by enhancing both intra-personal and inter-personal capacities.
Research cited in global education studies indicates that SEL programs lead to better academic performance, improved classroom climate, and a reduction in behavioral problems. In fact, one meta-analysis revealed that SEL participants showed an average academic gain equivalent to 11 percentile points compared to peers without SEL exposure.
Beyond academics, social and emotional learning shapes character. In workplaces, emotional intelligence is often ranked as highly as technical skill when evaluating candidates. Skills such as collaboration, adaptability, empathy, and conflict resolution are critical in industries where teamwork and communication drive results. SEL also plays a role in mental health, reducing stress and promoting self-esteem. By developing these capabilities early, learners are better prepared to meet the demands of higher education, careers, and civic engagement.
Educational Technology as a Catalyst for Social and Emotional Learning
While SEL can and does occur through traditional, in-person interactions, educational technology offers unique opportunities to expand, personalize, and sustain these experiences.
1. Encouraging Emotional Expression
Digital platforms—such as video journals, online discussion boards, and multimedia storytelling tools give students the ability to express thoughts and emotions at their own pace. This flexibility can be especially valuable for learners who are reluctant to speak up in class. For example, a student might use a voice recording to describe how a group project made them feel or use an image-based presentation to convey their reaction to a literature assignment. Such tools can serve as a safe outlet for emotional articulation, supporting self-awareness and communication.
2. Real-Time Emotional Insights
Some platforms integrate daily or weekly “check-in” features where learners can rate their mood, select from emotion icons, or respond to short prompts. Educators can view aggregated results to spot patterns—such as increased anxiety before exams—and provide timely support. This approach also empowers students to reflect on their own emotional states, a core component of emotional regulation.
3. Collaborative Learning Beyond the Classroom
Educational technology enables collaboration across distances, connecting students from different locations or cultures. Tools such as shared digital workspaces, real-time co-editing platforms, and online project boards allow for joint problem-solving and idea exchange. These experiences strengthen relationship skills, encourage respect for diverse viewpoints, and simulate the kinds of teamwork scenarios common in modern workplaces.
4. Simulating Real-World Social Scenarios
Virtual reality (VR) and gamified environments can immerse learners in realistic, emotionally charged situations—such as negotiating a community dispute, making decisions in a leadership role, or experiencing daily life from another person’s perspective. These simulations give learners a risk-free environment to practice empathy, ethical reasoning, and responsible decision-making.
Integrating Social-Emotional Learning into Digital Learning Environments
To successfully integrate SEL with educational technology, intentional design and consistent reinforcement are essential.
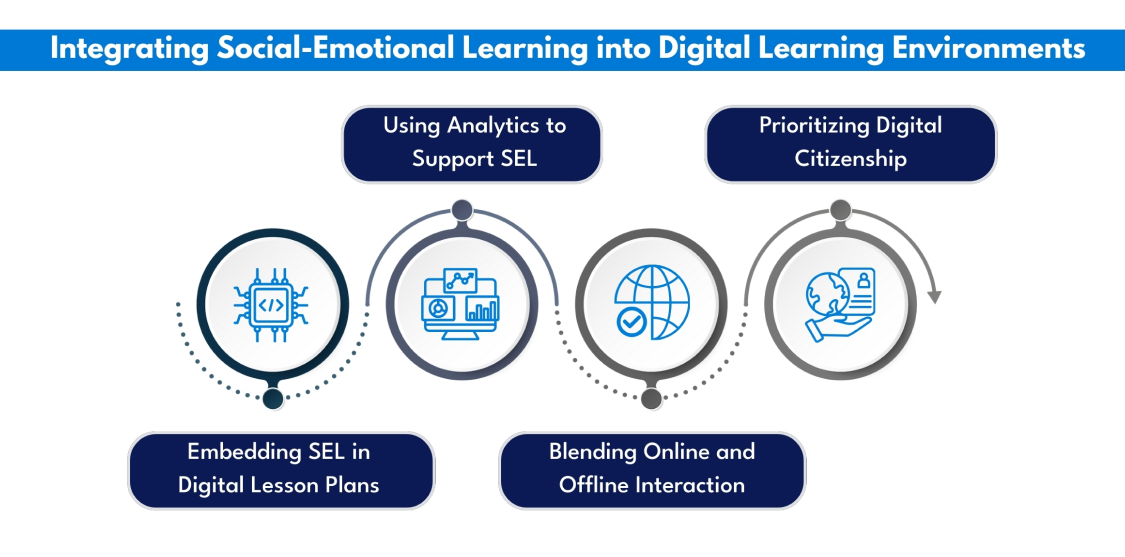
1. Embedding SEL in Digital Lesson Plans
Rather than treating SEL as a separate subject, it can be woven into existing curriculum activities. For example, a history assignment could include a reflective component where students consider how historical figures might have felt in their circumstances, or how they themselves would act in similar situations.
2. Using Analytics to Support SEL
Modern learning management systems can track participation levels, peer interactions, and completion rates. When analyzed thoughtfully, these data points can indicate which students may be disengaged, isolated, or in need of additional emotional support. This data-driven insight aligns with research showing that early interventions improve both emotional well-being and academic outcomes.
3. Blending Online and Offline Interaction
Blended learning environments provide the best of both worlds: digital tools for flexibility and face-to-face interaction for building deeper personal connections. For instance, a group project may start online with brainstorming in a shared document, then transition to an in-person session for discussion and finalization.
4. Prioritizing Digital Citizenship
SEL integration must also include guidance on responsible online conduct. Lessons on digital citizenship help students apply empathy in virtual interactions, respond constructively to disagreements, and understand the ethical implications of their digital presence. As learners spend increasing amounts of time online, these skills become a core part of both SEL and lifelong civic responsibility.
Challenges in Merging Social-Emotional Learning and EdTech
Integrating SEL with technology is promising, but challenges must be addressed for successful outcomes:
- Screen Fatigue – Prolonged screen time can lead to reduced focus and emotional detachment. This makes it important to balance digital and offline SEL activities.
- Digital Divide – Not all learners have equal access to devices or high-speed internet, potentially creating inequities in SEL opportunities.
- Privacy Concerns – Emotional data must be handled with strict confidentiality and informed consent. Mismanagement can undermine trust.
- Overemphasis on Metrics – While analytics can guide instruction, reducing SEL to numerical scores risks oversimplifying complex emotional growth.
Addressing these barriers requires equitable access policies, professional development for educators, and ethical data governance.
The Long-Term Impact of Social and Emotional Learning Through Technology
When thoughtfully implemented, SEL via educational technology produces benefits that extend far beyond the classroom.
1. Academic Advancement
Technology-enabled SEL promotes deeper engagement, more meaningful collaboration, and greater motivation. These factors contribute directly to improved academic results, as learners are more focused and invested in their studies.
2. Emotional Resilience
Regular practice in emotional regulation, empathy, and reflection prepares students to adapt to change, manage setbacks, and maintain well-being in high-pressure situations.
3. Workplace Readiness
In professional settings, skills such as active listening, adaptability, and collaboration are essential. By simulating workplace-like scenarios and encouraging teamwork through digital tools, students gain practical experience before entering the workforce.
4. Social Cohesion
Technology can connect learners from different cultural and social backgrounds, promoting empathy, breaking down stereotypes, and building understanding across boundaries. These connections help prepare students to participate constructively in an increasingly interconnected world.
Key SEL Strategies for Effective Implementation
For SEL to be effectively integrated into technology-enhanced learning, educators and institutions can follow these strategies:
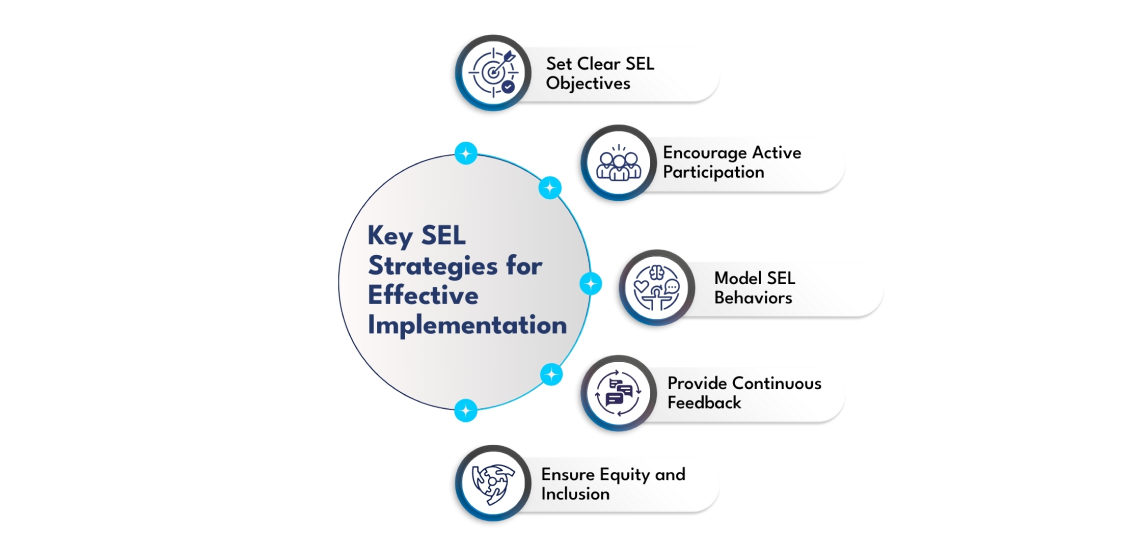
- Set Clear SEL Objectives – Define which competencies will be emphasized and ensure all activities contribute to these goals.
- Encourage Active Participation – Design activities that require learners to apply SEL skills, such as peer feedback exercises or group decision-making tasks.
- Model SEL Behaviors – Teachers should demonstrate empathy, respect, and active listening within both physical and digital learning environments.
- Provide Continuous Feedback – Offer regular, constructive feedback on both academic progress and SEL development.
- Ensure Equity and Inclusion – Guarantee access to devices and internet for all students, and adapt materials for diverse learning needs.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Social and Emotional Learning in a Digital Era
As artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and advanced analytics evolve, SEL will likely become even more personalized. AI could identify emotional cues from student interactions, recommend targeted activities, or connect learners to resources that support their emotional needs. Augmented and virtual reality could make empathy-building exercises more immersive, placing learners in scenarios that challenge their perceptions and understanding.
However, the human element will remain central. Technology should enhance human connection, not replace it. SEL’s ultimate goal is to prepare individuals for meaningful participation in society—a task that requires both innovative tools and genuine human relationships.
Conclusion
Social and Emotional Learning is not a peripheral component of education—it is the foundation on which academic achievement, personal well-being, and societal harmony are built. By merging SEL with educational technology, we create opportunities to develop emotional intelligence in innovative, accessible, and impactful ways.
In this intersection of empathy and innovation, learners gain the skills to navigate complex social landscapes, manage personal challenges, and contribute positively to their communities. As we continue to refine digital tools and integrate them thoughtfully, the vision of a connected, emotionally intelligent, and compassionate generation becomes not just possible, but achievable.
Latest
Trends blogs
- From Vision to Impact: Closing the Gender Gap in STEM Education
- Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and the Future of Human-Centered Education
- Mid-Career Education in a Changing Labor Market
- The Next Phase of STEM Education: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Classroom Curricula





