The evolution of the education sector, from ancient educational systems to modern virtual classrooms, highlights the constant pursuit of knowledge. While methods have changed, the goal of learning remains steadfast. Traditional rote memorization methods, though once dominant, have often fallen short in promoting deep understanding and practical application of knowledge. Cognitive Learning Theory emerged as a response to these shortcomings, emphasizing the importance of thinking about the learning process itself.
Cognitive Learning Theory centers on metacognition, or "thinking about thinking." This approach transforms learning into a dynamic and engaging lifelong pursuit rather than a routine, automatic activity. By focusing on how we learn, cognitive learning encourages a deeper, more reflective engagement with material.
Both educational institutions and the corporate sector are incorporating cognitive learning strategies. In schools and colleges, this approach helps students retain information longer and apply knowledge effectively. Similarly, in the corporate world, cognitive learning programs enhance employees' efficiency and enable them to apply relevant skills to specific tasks, contributing to organizational success.
What is Cognitive Learning?
Cognitive learning is an active style of learning that focuses on helping individuals maximize their brain's potential. It facilitates the connection of new information with existing ideas, thereby deepening memory and retention.
Cognitive learning goes beyond memorization, encouraging a deeper understanding of the material, which in turn improves the ability to apply knowledge in real-world situations. It is thus, the brain's mental processes to absorb and retain information through senses, experiences, and active thoughts.
Cognitive Learning Theories
Cognitive learning theory explores how internal and external factors influence an individual's mental processes to enhance learning. When cognitive processes like attention, observation, memory retrieval, and categorization are functioning properly, learning is more effective.
Several researchers have significantly contributed to this theory:
- Jean Piaget: Piaget emphasized that both the environment and internal cognitive structures play critical roles in learning. He believed that knowledge is actively constructed by learners based on their existing cognitive frameworks.
- Jerome Bruner: Bruner focused on how mental processes are linked to teaching, advocating for learning that involves active problem-solving and critical thinking.
Types of Cognitive Learning Theories
Here are the cognitive learning theories that enhance deeper understanding and application of knowledge.
-
Social Cognitive Theory:
This theory, primarily developed by Albert Bandura, examines how people are influenced by and interact with their environment. Observational learning, a key component, involves learning by watching others, which can quickly impart both positive and negative behaviors. -
Cognitive Behavioral Theory:
This theory delves into the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It posits that our thoughts influence our emotions and behaviors, and by changing our thought patterns, we can alter our emotional responses and actions.
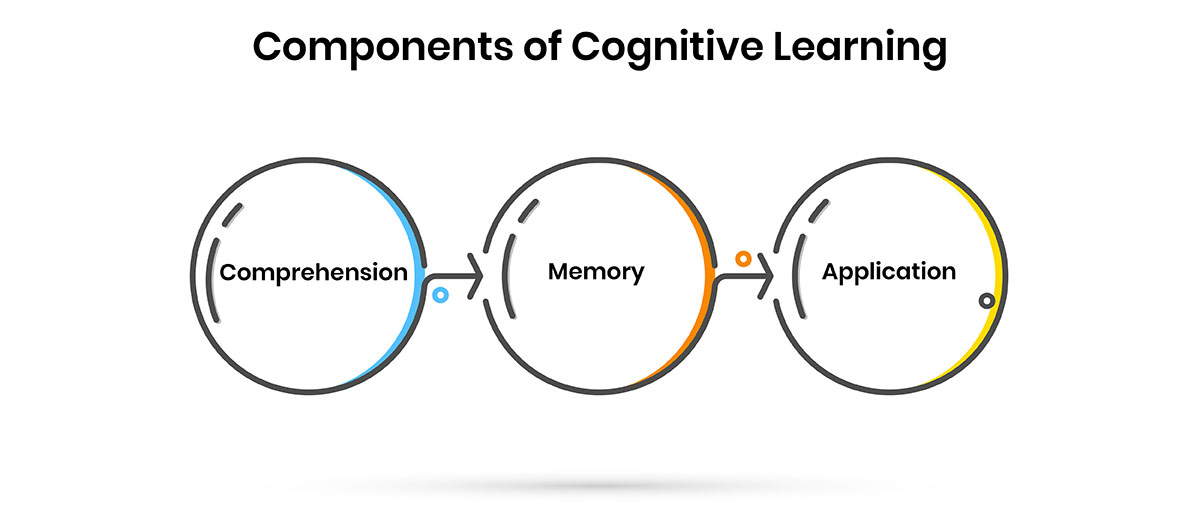
Components of Cognitive Learning
Let’s explore the foundational elements that drive effective cognitive learning strategies and outcomes. It comprises three fundamental aspects:
-
1. Comprehension:
Understanding the purpose behind learning a specific subject is crucial. This awareness enhances the ability to grasp new concepts. -
2. Memory:
Cognitive learning discourages cramming, instead promoting a deep understanding of the subject matter, which aids in connecting new knowledge with previous experiences. -
3. Application:
Strategies in cognitive learning help apply new information or skills to real-life situations, fostering problem-solving abilities.
The Role of Metacognition
Metacognition involves reflecting on one's learning processes to understand and improve them. It is central to cognitive learning theory, as it allows learners to guide their thoughts and optimize their learning strategies. By mastering metacognition, individuals can enhance their comprehension and problem-solving skills, making learning a continuous and engaging pursuit.
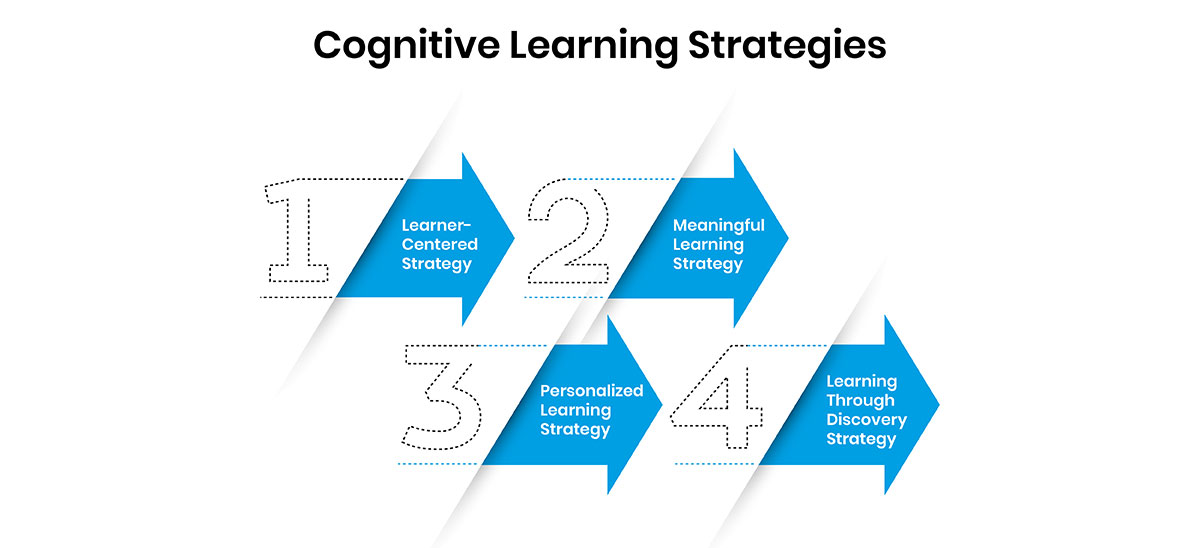
Strategies of Cognitive Learning Theory
Cognitive learning theory emphasizes understanding the processes involved in learning and how to enhance them. Various strategies have been developed to apply this theory effectively in educational and corporate environments. Here are the key strategies:
-
1. Learner-Centered Strategy
This approach places the learner at the core of the educational process, integrating their existing knowledge, experiences, and ideas. Learning begins with foundational knowledge and deepens over time through three main components:
- Accommodation: Adjusting new information by altering existing cognitive structures.
- Assimilation: Integrating new concepts into the learner's existing knowledge framework.
- Equilibrium: Balancing new information with prior knowledge to maintain cognitive stability.
In a corporate setting, training programs should be designed to build on what employees already know, providing analogies and practical tasks to connect new information with existing knowledge. Encouraging questions and comments is essential to this strategy.
-
2. Meaningful Learning Strategy
This strategy contrasts with rote memorization by focusing on the meaningful acquisition of knowledge. It involves presenting new material in a way that connects it to the learner's existing knowledge base, enhancing comprehension and retention. Key elements include:
- Relevance: Ensuring the material is closely related to what the learner already knows.
- Sequence: Introducing new information in a logical order to build on prior knowledge.
- Active Learning: Engaging learners in activities that cultivates a deeper understanding and a strong teacher-student relationship.
Incorporating background information and ensuring each session's relevance to the learner's tasks are crucial for effective meaningful learning.
-
3. Personalized Learning Strategy
Recognizing the uniqueness of each learner, this strategy tailors the learning experience to individual needs, strengths, and gaps. It involves creating a customized action plan to optimize the learner's strengths and address weaknesses.Modern technologies like AI recommendations and machine learning can enhance personalized learning by providing customized content and learning paths. Digital learning assistants can identify employees' skills and suggest relevant next steps, making learning more efficient and targeted.
-
4. Learning Through Discovery Strategy
This strategy promotes exploration and active engagement in learning, allowing learners to build knowledge independently. It enhances analytical skills and prepares learners to solve real-world problems by encouraging them to:
- Explore: Actively seek out new ideas and knowledge.
- Analyze: Develop problem-solving skills by facing real-world challenges.
- Reflect: Continuously review and integrate new knowledge with existing cognitive structures.
This strategy can be implemented by challenging students or employees with new tasks and encouraging them to solve problems independently.
Benefits of Cognitive Learning Theory
The implementation of cognitive learning theory in the education system and corporate environments brings numerous positive changes. Here are some of the major benefits:
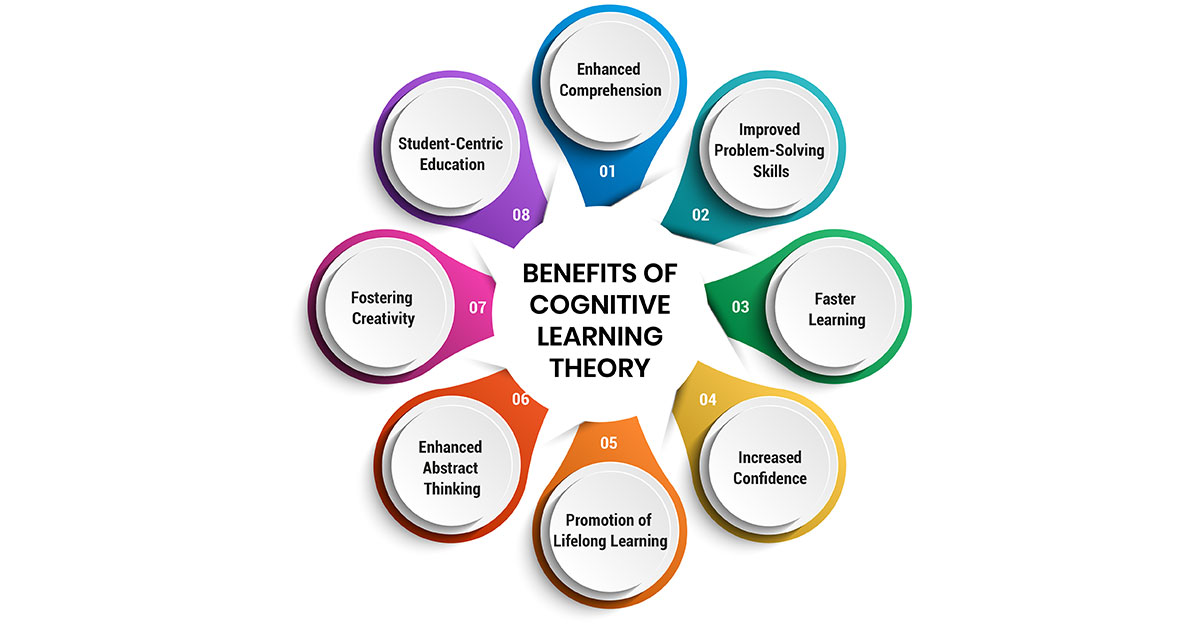
- 1. Enhanced Comprehension Cognitive learning theory significantly improves learners’ understanding of new materials. By engaging in hands-on learning processes, students and employees can achieve a deeper comprehension of subjects. This approach builds on previous knowledge, allowing learners to integrate new information effectively, leading to a more thorough grasp of complex concepts.
- 2. Improved Problem-Solving Skills One of the key advantages of cognitive learning is the enhancement of problem-solving abilities. Learners are taught how to approach and resolve issues analytically, equipping them with the skills needed to tackle real-life challenges. By understanding how to learn, individuals can apply these skills to various situations, developing better decision-making and innovation.
- 3. Faster Learning Cognitive learning strategies facilitate faster acquisition of knowledge. Unlike traditional memorization methods, this approach breaks down complex ideas into simpler, more understandable components. By building on existing knowledge, learners can quickly grasp new concepts and apply them efficiently. This iterative learning process accelerates the overall learning pace.
- 4. Increased Confidence Implementing cognitive learning principles boosts learners' confidence. As individuals gain a deeper understanding of new topics and develop problem-solving skills, they feel more capable of approaching and mastering challenging tasks. This increased self-assurance encourages learners to explore new areas and take on more complex projects with confidence.
- 5. Promotion of Lifelong Learning Cognitive learning inculcates a love for learning that extends beyond formal education. By making learning engaging and relevant, this approach encourages learners to continuously seek knowledge and skills throughout their lives. The emphasis on understanding rather than memorization makes education enjoyable and motivates learners to remain curious and proactive in their learning journeys.
- 6. Enhanced Abstract Thinking For teachers and trainers, cognitive learning theory enhances abstract thinking. Educators can develop and convey concepts more effectively, stimulating creativity and innovation among students. This ability to perceive and interpret information abstractly helps both teachers and learners to understand and solve problems more creatively.
- 7. Fostering Creativity By encouraging concept formation and perceptual skills, cognitive learning promotes creativity. Learners are better equipped to break down complex issues and think outside the box, leading to innovative solutions. This creative problem-solving ability is invaluable in both educational settings and the workplace.
- 8. Student-Centric Education Cognitive learning makes education more student-centric, addressing the unique needs and perspectives of each learner. By focusing on active learning and personal engagement, this approach helps reduce dropout rates and keeps students motivated. The strategies used in cognitive learning make education fun and exciting, encouraging a positive attitude towards learning.
Conclusion
Cognitive Learning Theory revolutionizes education and corporate training by prioritizing understanding over Parrot-fashion learning. This theory's focus on metacognition, comprehension, and personalized strategies not only enhances problem-solving skills but also fosters a genuine love for learning. By tailoring educational experiences to individual needs and encouraging active engagement, cognitive learning strategies prepare learners to tackle real-world challenges with confidence and creativity. The result is a dynamic, student-centric approach that promotes lifelong learning and continuous personal and professional growth.
Latest
Trends blogs
- From Vision to Impact: Closing the Gender Gap in STEM Education
- Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and the Future of Human-Centered Education
- Mid-Career Education in a Changing Labor Market
- The Next Phase of STEM Education: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Classroom Curricula
Focus blogs
- Research-Driven Education: Strengthening Strategies, Policies, and Classroom Practice
- Professional Certifications for Career Growth: What Students and Young Professionals Need to Know
- Building a High-Impact Center of Excellence: What You Need to Know
- Beyond Graduation: The Importance of Lifelong Learning in Higher Education





